
SANOclav Laboratory autoclave LaM320MCSJ, 4.430,96€
1. Autoclave. The etymology of autoclave is auto (self) and clave (closing with a clanking sound). To understand the autoclave, the concepts of vaporization pressure and boiling point should be comprehended first: If liquid is placed in a container in an enclosed space, it is evaporated and then returns, thus repeating condensation into water.

New 400 Litre Autoclave Introduced Labmate Online
Dasar Teori Autoklaf (Autoclave) Autoklaf (autoclave) adalah alat untuk mensterilkan berbagai macam alat dan bahan yang digunakandalam mikrobiologi dengan menggunakan uap air jenuh yang bertekanan tinggi. Tekanan yang digunakan pada umumnya sebesar 15 Psi atau 1 atm dengan suhu 121,5 oC (250oF) dan bisa mencapai 650 oC.

BIOCLAVE™ 28 Research Sterilizer Autoclave 28 Liter 220V
Within an autoclave, steam pressure can build to 15 to 30 lb per square inch above atmospheric pressure, bringing the temperature up with it to 121 to 123°C. Steam is wet and penetrative to begin with, even at 100°C (the boiling point of water). When raised to a high temperature and driven by pressure, it penetrates thick substances that.

Pengenalan Jenis dan Fungsi Alatalat Laboratorium Mikrobiologi Generasi Biologi
autoclave to effectively treat medical waste according to accepted treatment standards. BASIC PRINCIPLES AND GENERAL APPROACH Treatment efficacy refers to the capability of an autoclave to alter waste such that its potential for transmitting disease is eliminated or substantially decreased. The terms disinfection and sterilization are often

What is an Autoclave? (with pictures)
Pemanfaatan Autoclave Model 1925x Sebagai Alat Suling dengan Model. Sterilisasi (mikrobiologi) Alqum dan N. Tarsono G./Vol 2 (1) 2019, 34-40 . ISSN 2655 4887 (Print),ISSN 2655 1624 (Online) 35. INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF LABORATORY . membunuh mikroorganisme, melainkan

BioClave 16 Digital BenchTop Autoclave 16L by Benchmark Scientific
Priorclave Autoclaves for Microbiology Labs. Many microbiology labs find that Priorclave's autoclaves are the best choice for them. That's because our autoclaves are built for research, with an ASME-stamped 316L stainless steel pressure chamber and full programmability. Our steam autoclaves are each custom built in our south London factory.
Autoclave Sterilization Principle, Procedure, Types, Uses • Microbe Online
Dalam bidang mikrobiologi, fungsi autoclave juga memegang peranan penting. Sebagai contoh dalam proses pembiakan mikroba dibutuhkan media, baik media cair, media semi padat maupun media padat. Nah, bukan hanya sterilisasi di awal sebelum penggunaan, setelah pengamatan mikroba baiknya dilakukan sterilisasi juga sebelum media tersebut dibuang.

Benchtop Autoclaves for Laboratory Microbiology International
Autoclaves or sterilizers are vessels that use pressurized steam to eradicate micro-organisms. Their purpose in the microbiology laboratory is either to prepare culture media, reagents and equipment. or for decontaminating biohazardous waste materials. Whilst sterilization can be achieved using a number of techniques: irradiation [UV and other.

Microbiology from A to Z explained Micropia Micropia
An autoclave is a machine that utilizes moist heat in the form of saturated steam under pressure to achieve sterilization. It is widely used in various industries, including healthcare facilities and laboratories, for its ability to destroy microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores.

A Guide to Sterilising Equipment How Autoclaves Work [BLOG POST] MES
The usual procedure is to heat at 1.1 kilograms/square centimeter (kg/cm 2) [15 pounds/square inch (lb/in 2 )] steam pressure, which yields a temperature of 121°C. At 121°C, the time of autoclaving to achieve sterilization is generally considered to be 15-20 min, depending on the volume of the load.

Benchtop Autoclaves for Laboratory Microbiology International
Autoclaves are relatively safe and easy to operate and extremely effective at killing microbial vegetative cells and spores. Similar to home pressure cookers, which create pressure and high temperatures to shorten cooking times, autoclaves use super-heated steam under pressure to kill microbes. Sterilizing temperatures are usually 121-127°C.
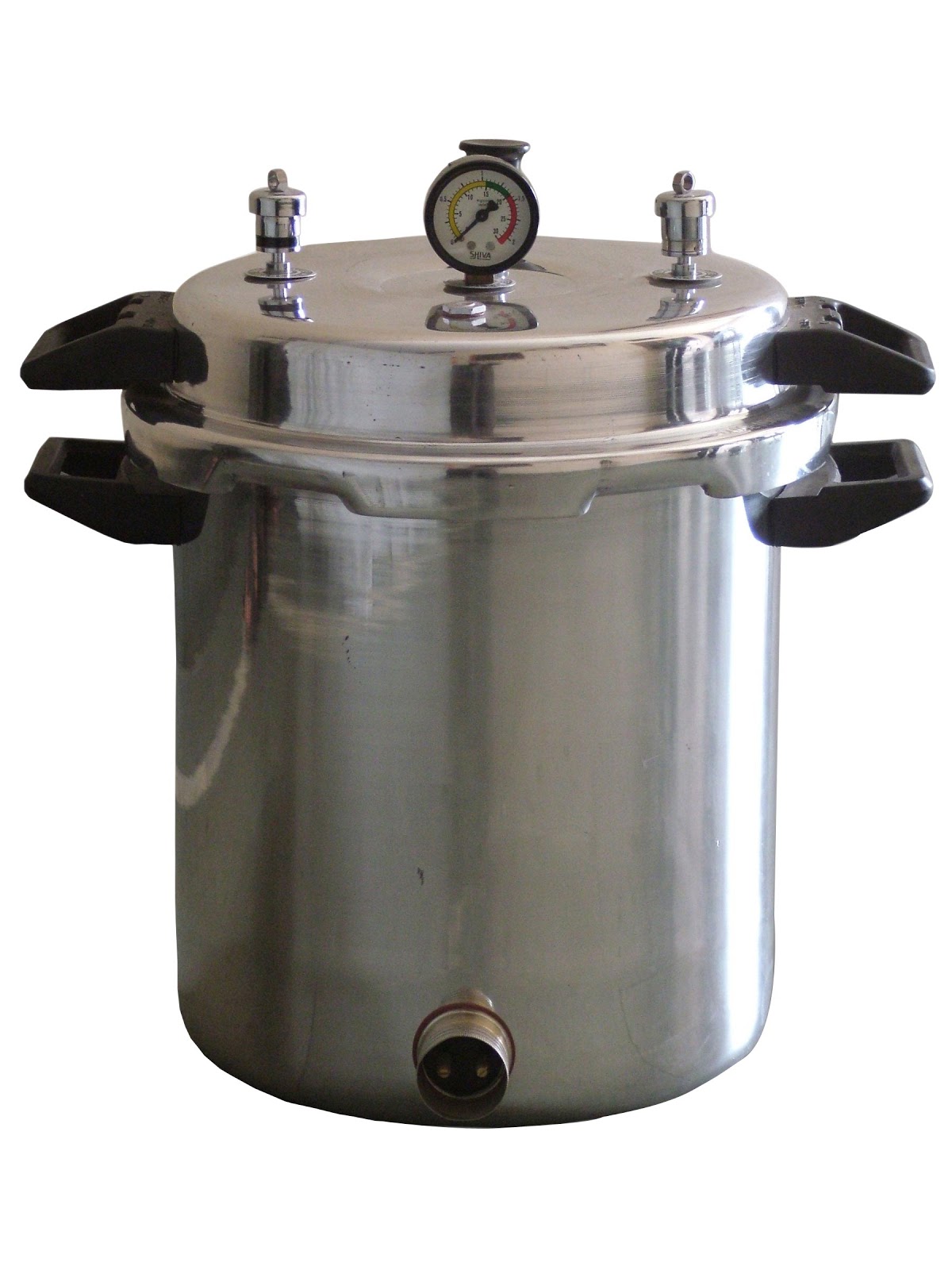

BioResource Sterilization Autoclaving
Abstract. Sterilization and disinfection are the basic components of hospital infection control activities. Every day, a number of hospitals are performing various surgical procedures. Even more number of invasive procedures are being performed in different health care facilities. The medical device or the surgical instrument that comes in.

Autoclave Principle, Types, and Precautions Plant Cell Technology Your partner in plant
609-258-9527. Top. m. Autoclaves provide a physical method for disinfection and sterilization. They work with a combination of steam, pressure and time. Autoclaves operate at high temperature and pressure in order to kill microorganisms and spores. They are used to decontaminate certain biological waste and sterilize media, instruments and lab.
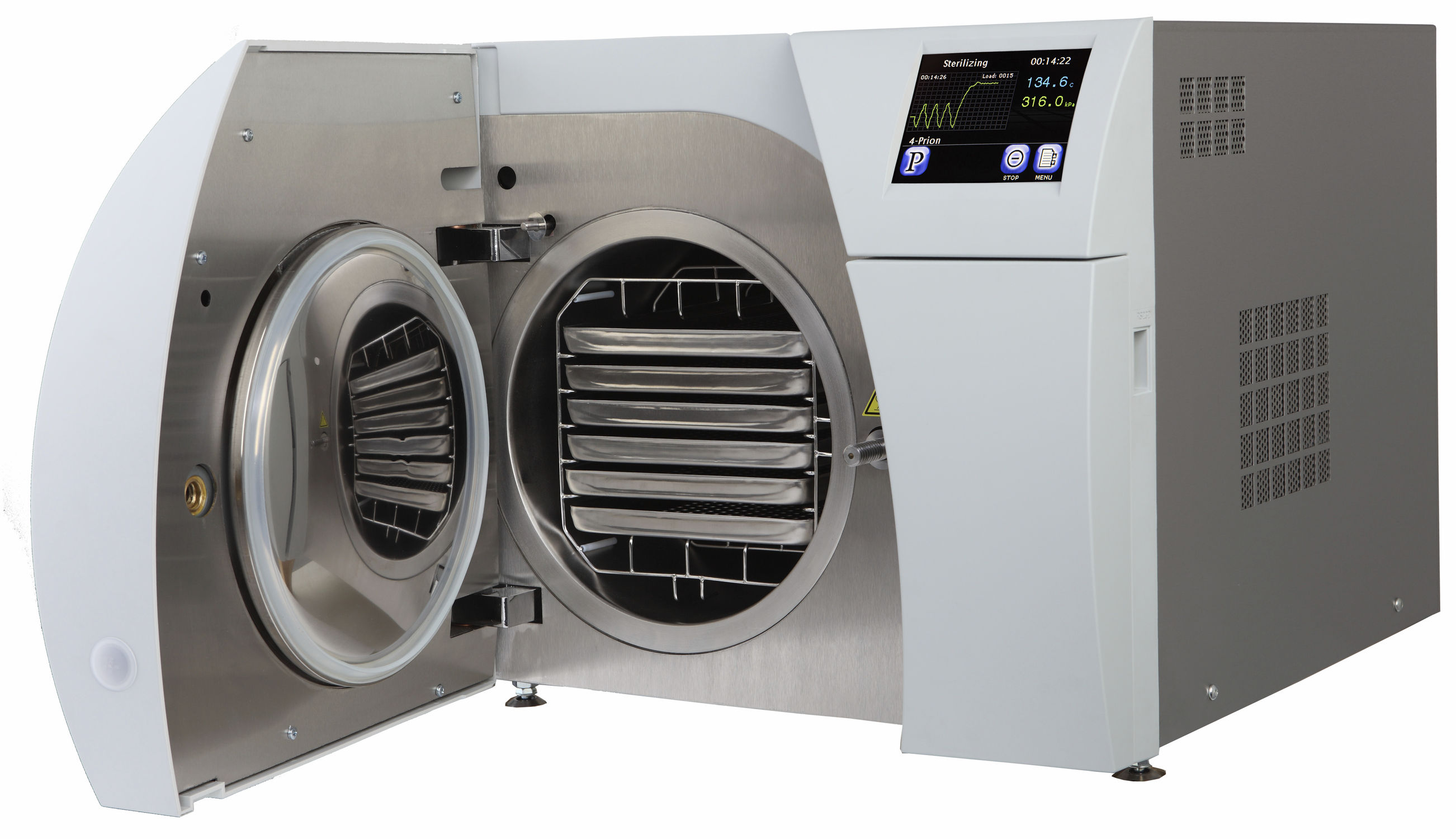

How Does an Autoclave Work How to Use Autoclaves?
Autoclave in microbiology The identification of pathogens and germs is at the foreground of the demanding work in a microbiology laboratory. Every day, a large number of experiments are carried out in the laboratory for this purpose. Extremely diverse culture media are produced, containers and fluids need to be autoclaved and contaminated waste needs to be deactivated. The […]

How Are Autoclaves Used In Microbiology? MES Australia
Everything About Autoclaves What is an autoclave? Autoclaves are also known as steam sterilizers, and are typically used for healthcare or industrial applications.An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores on items that are placed inside a pressure vessel.

BSL3 Autoclaves, Laboratory Autoclave Microbiology International
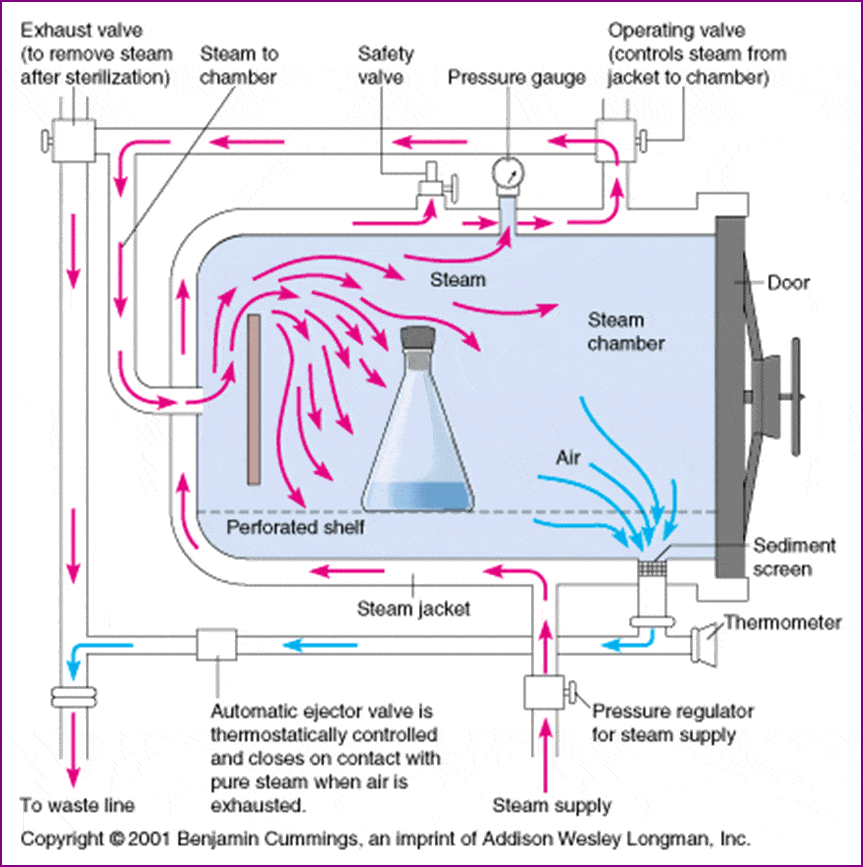
The two basic types of steam sterilizers (autoclaves) are the gravity displacement autoclave and the high-speed prevacuum sterilizer. In the former, steam is admitted at the top or the sides of the sterilizing chamber and, because the steam is lighter than air, forces air out the bottom of the chamber through the drain vent.